熟悉 JSON Schema:给 JSON 数据制定规则

JSON 是一种非常灵活的数据格式,正因为这种灵活性,同一份数据可以有很多种不同的表示方式。你可以用字符串表示数字,也可以用数字表示字符串;可以用数组包含不同类型的元素,也可以在对象中随意增减字段。
这种灵活性在某些场景下是优势,但在需要数据交换和验证的场景中却可能带来问题。JSON Schema 就是为了给 JSON 数据制定规则而设计的,它用 JSON 的语法来描述 JSON 数据应该遵循的结构和约束。
从 JSON 的灵活性说起
看一个简单的例子,下面这些都是合法的 JSON:
{"name": "张三", "age": 25}{"name": "张三", "age": "25"}{"username": "张三", "years": 25, "active": true}
从 JSON 格式的角度来说,这三个都没有问题。但如果你需要处理这些数据,就会发现麻烦了:age 字段有时是数字,有时是字符串;字段名也不统一;有些数据多了一些字段,有些又少了一些字段。
JSON Schema 可以定义一套规则,明确说明什么样的 JSON 数据是符合要求的。比如:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"age": {"type": "integer"}
},
"required": ["name", "age"],
"additionalProperties": false
}
这个 Schema 规定了:数据必须是对象类型,包含 name(字符串)和 age(整数)两个字段,不允许其他字段存在。
基本的类型约束
JSON Schema 最基础的功能是类型约束。JSON 支持的基本数据类型在 Schema 中都有对应的约束方式。
type 关键字用来指定数据类型:
{"type": "string"} // 字符串
{"type": "number"} // 数字(包含整数和小数)
{"type": "integer"} // 整数
{"type": "boolean"} // 布尔值
{"type": "array"} // 数组
{"type": "object"} // 对象
{"type": "null"} // null 值
你也可以指定多个可能的类型:
{"type": ["string", "number"]}这个规则允许数据是字符串或数字。
对于字符串类型,可以进一步限制内容特征:
{
"type": "string",
"minLength": 1,
"maxLength": 100,
"pattern": "^[a-zA-Z]+$"
}这个规则要求字符串长度在 1-100 个字符之间,而且只能包含英文字母。
数字类型可以设置取值范围:
{
"type": "number",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 100,
"exclusiveMaximum": true
}这个规则要求数字大于等于 0,小于 100(不包含 100)。
约束数组结构
数组是 JSON 中常用的数据结构,JSON Schema 提供了多种方式来约束数组。
最简单的是限制数组元素的类型和数量:
{
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"minItems": 1,
"maxItems": 5,
"uniqueItems": true
}这个规则要求数组包含 1-5 个字符串元素,而且每个元素都必须唯一。
如果数组中不同位置的元素有不同的约束,可以用数组形式的 items:
{
"type": "array",
"items": [
{"type": "string"},
{"type": "number"},
{"type": "boolean"}
],
"minItems": 3,
"maxItems": 3
}这个规则要求数组恰好包含 3 个元素:第一个是字符串,第二个是数字,第三个是布尔值。
约束对象结构
对象是 JSON 中最复杂的数据类型,JSON Schema 提供了丰富的约束选项。
properties 用来定义对象的属性:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {"type": "integer"},
"name": {"type": "string"},
"active": {"type": "boolean"}
}
}required 指定哪些属性是必需的:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {"type": "integer"},
"name": {"type": "string"},
"email": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["id", "name"]
}这个规则要求 id 和 name 必须存在,email 是可选的。
additionalProperties 控制是否允许未定义的属性:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"}
},
"additionalProperties": false
}设置为 false 后,对象只能包含 properties 中定义的属性。如果你想允许额外属性但要约束它们的类型,可以这样写:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"}
},
"additionalProperties": {"type": "string"}
}这样,除了 name 字段外,其他字段必须都是字符串类型。
更精确的值约束
除了类型约束,JSON Schema 还支持更精确的值约束。
enum 限制字段只能取特定的值:
{
"type": "string",
"enum": ["pending", "processing", "completed", "cancelled"]
}const 要求字段必须是特定的值:
{"const": "success"}
对于字符串,format 提供了常用格式的验证:
{"type": "string", "format": "email"}
{"type": "string", "format": "uri"}
{"type": "string", "format": "date"}
{"type": "string", "format": "date-time"}
{"type": "string", "format": "ipv4"}组合约束条件
有时候需要更复杂的约束逻辑,JSON Schema 提供了逻辑组合关键字。
anyOf 表示满足其中任意一个条件:
{
"anyOf": [
{"type": "string", "maxLength": 5},
{"type": "number", "minimum": 0}
]
}allOf 表示必须同时满足所有条件:
{
"allOf": [
{"type": "string"},
{"minLength": 2},
{"maxLength": 10}
]
}oneOf 表示只能满足其中一个条件:
{
"oneOf": [
{"type": "number", "multipleOf": 5},
{"type": "number", "multipleOf": 3}
]
}not 表示不能满足指定条件:
{
"type": "string",
"not": {"enum": ["admin", "root"]}
}引用和模块化
当 Schema 变得复杂时,可以使用引用来避免重复定义。
{
"$defs": {
"person": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"age": {"type": "integer"}
},
"required": ["name"]
}
},
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"author": {"$ref": "#/$defs/person"},
"reviewer": {"$ref": "#/$defs/person"}
}
}这样,person 的定义可以在多个地方重复使用。
你也可以引用外部文件中的 Schema:
{"$ref": "https://example.com/schemas/person.json"}条件约束
JSON Schema 还支持条件约束,根据某些字段的值来决定其他字段的约束规则:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"type": {"enum": ["personal", "business"]},
"name": {"type": "string"},
"company": {"type": "string"},
"taxId": {"type": "string"}
},
"if": {
"properties": {"type": {"const": "business"}}
},
"then": {
"required": ["company", "taxId"]
},
"else": {
"not": {
"anyOf": [
{"required": ["company"]},
{"required": ["taxId"]}
]
}
}
}这个规则表示:如果 type 是 "business",那么 company 和 taxId 是必需的;否则这两个字段不应该存在。
在 Apifox 中应用 JSON Schema
了解了 JSON Schema 的基本语法后,你会发现在 Apifox 中使用它非常直观。
Apifox 原生支持 JSON Schema,你可以直接在接口定义中使用完整的 Schema 语法。
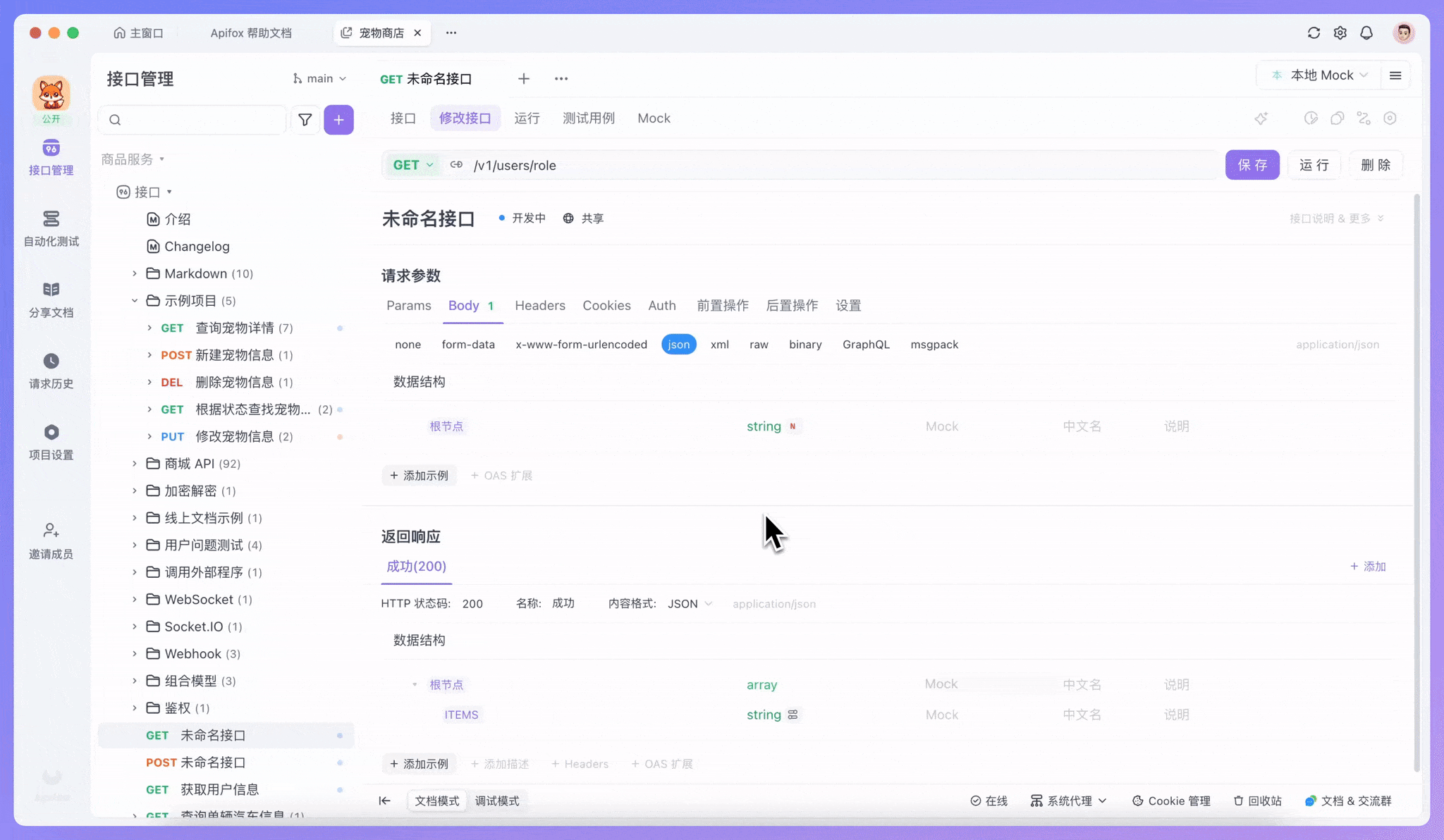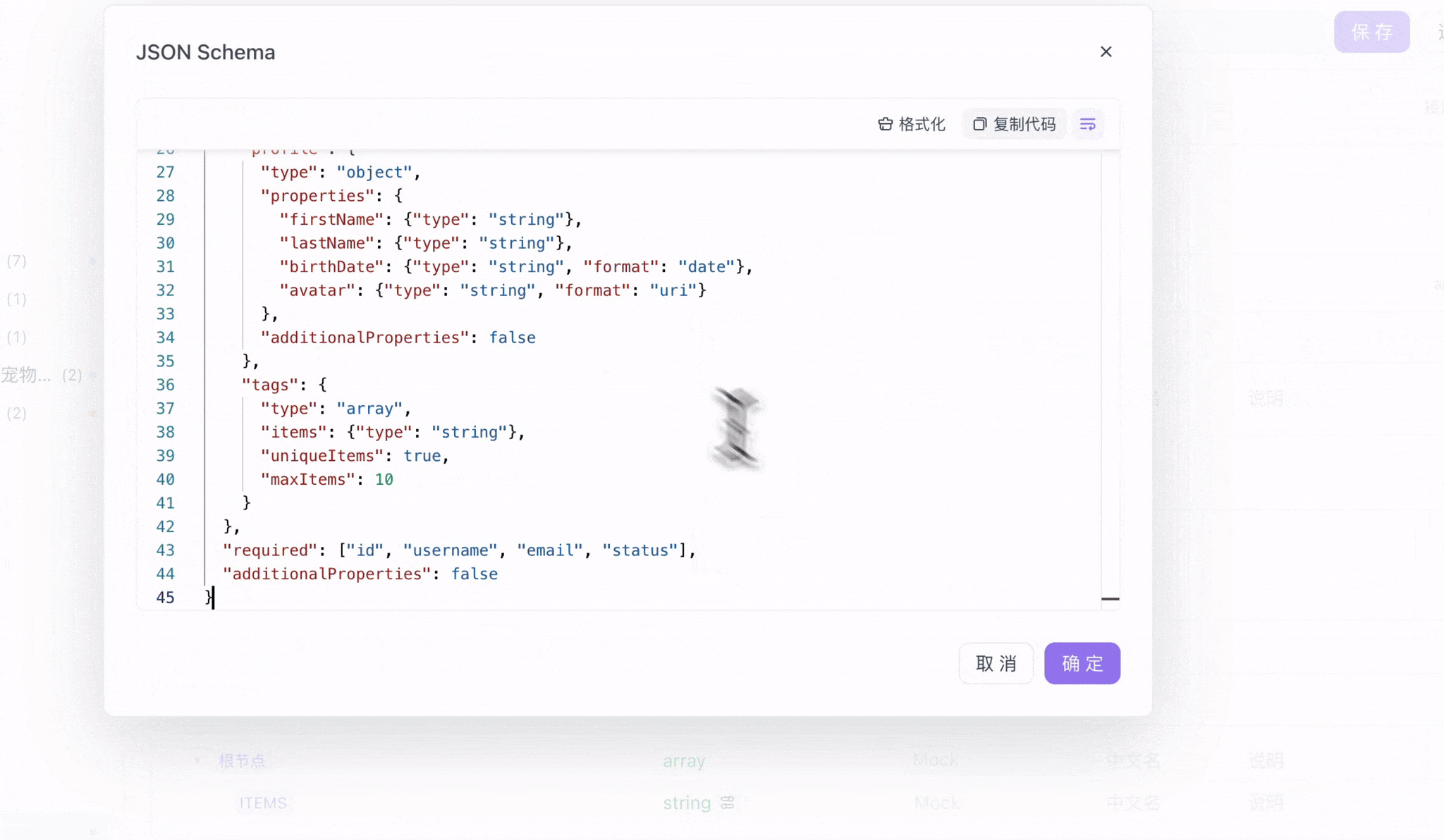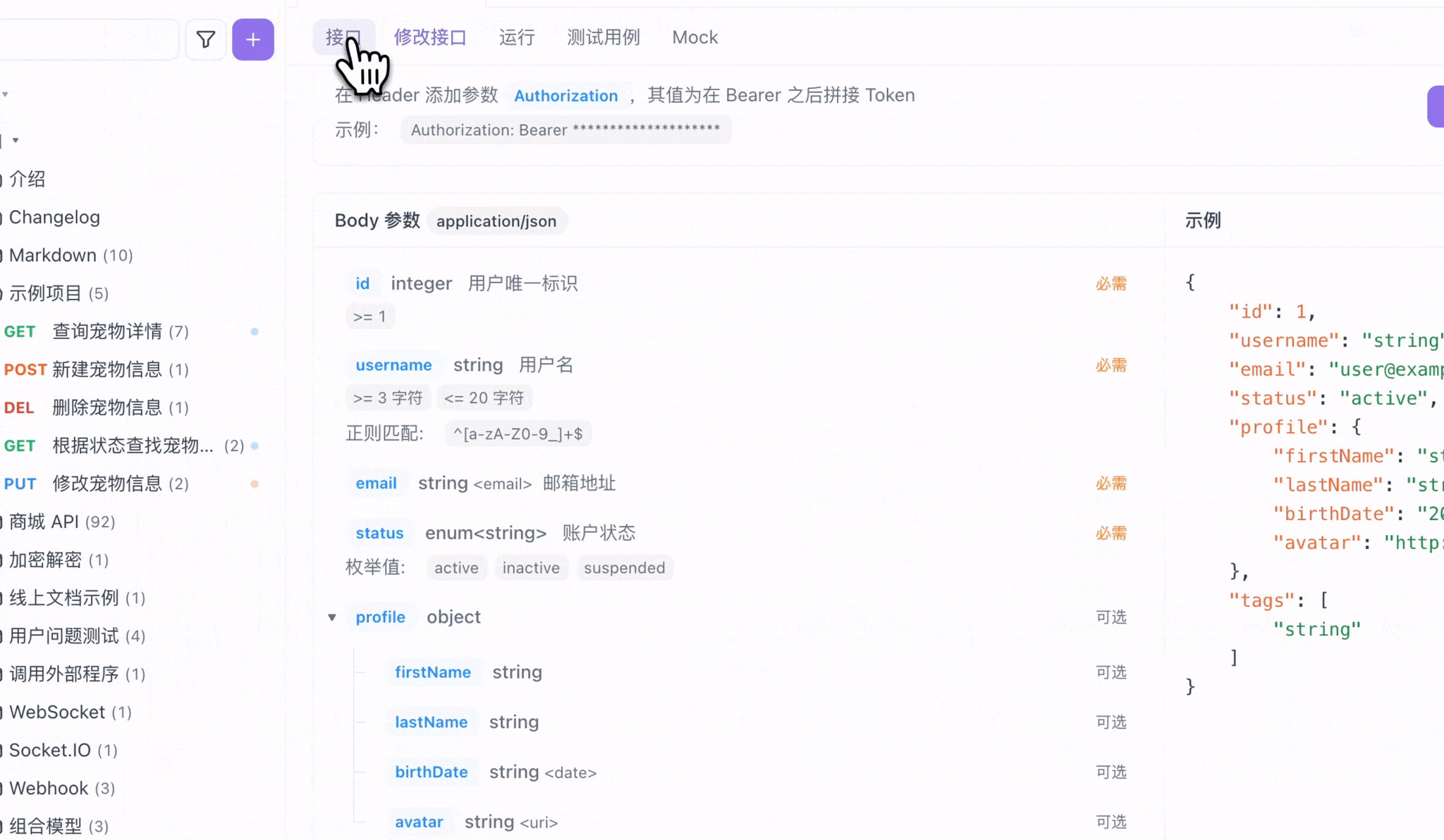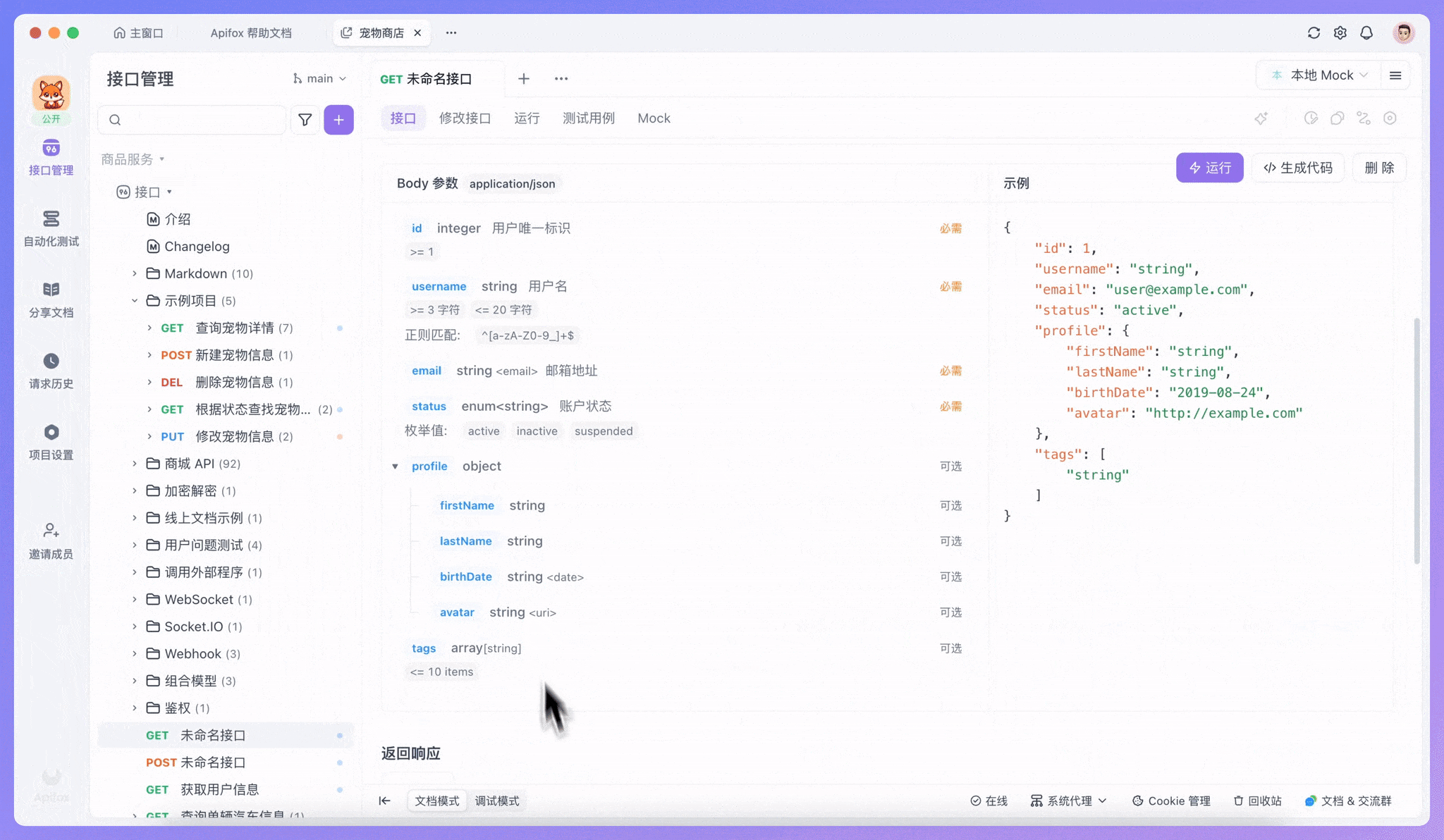
当你创建接口时,可以在请求体或响应体的 Schema 编辑器中直接编写 JSON Schema 代码。比如定义一个用户数据的结构:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"description": "用户唯一标识"
},
"username": {
"type": "string",
"minLength": 3,
"maxLength": 20,
"pattern": "^[a-zA-Z0-9_]+$",
"description": "用户名"
},
"email": {
"type": "string",
"format": "email",
"description": "邮箱地址"
},
"status": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["active", "inactive", "suspended"],
"description": "账户状态"
},
"profile": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"firstName": {"type": "string"},
"lastName": {"type": "string"},
"birthDate": {"type": "string", "format": "date"},
"avatar": {"type": "string", "format": "uri"}
},
"additionalProperties": false
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"uniqueItems": true,
"maxItems": 10
}
},
"required": ["id", "username", "email", "status"],
"additionalProperties": false
}Apifox 会根据这个 Schema 自动生成清晰的文档界面,显示每个字段的类型、约束条件和说明。同时,它还能根据 Schema 生成符合规则的 Mock 数据用于测试。
数据模型的复用
Apifox 的数据模型功能让 JSON Schema 的复用变得更简单。你可以创建通用的数据模型,然后在多个接口中引用:
{
"User": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {"type": "integer"},
"username": {"type": "string"},
"email": {"type": "string", "format": "email"}
},
"required": ["id", "username", "email"]
},
"ApiResponse": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"code": {"type": "integer"},
"message": {"type": "string"},
"data": {}
},
"required": ["code", "message"]
}
}
然后在具体接口中可以这样使用:
{
"allOf": [
{"$ref": "#/components/schemas/ApiResponse"},
{
"properties": {
"data": {"$ref": "#/components/schemas/User"}
}
}
]
}这样就创建了一个包含用户数据的标准 API 响应格式。
自动化验证和测试
基于 JSON Schema 的定义,Apifox 可以自动验证接口的请求和响应数据是否符合规范。当你发送测试请求时,如果返回的数据不符合 Schema 定义,Apifox 会明确指出哪些字段不符合要求。
这种自动化验证可以帮你及时发现数据格式的问题,避免因为数据结构不一致而导致的 Bug。特别是在接口较多的项目中,手动检查每个接口的数据格式是不现实的,JSON Schema 的自动验证就显得特别有价值。
JSON Schema 本质上是一套描述 JSON 数据结构的规则语言。掌握了它的语法和特性,你就能精确地定义数据应该有什么样的结构和约束,让数据的生产者和消费者都能按照统一的标准来处理数据。






